In situations where the female partner is not ovulating, clomiphene citrate (Clomid® or Serophene®) is often the first line treatment to restore ovulation. Clomiphene causes the pituitary gland in the brain to produce more Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) than happens in the natural cycle; this in turn stimulates the ovaries to produce more eggs.
It is usually administered between day 2 and 6 of the menstrual cycle. In women who have very irregular periods a progesterone medication such as Primolut® or Provera® may be administered for 10 days prior the commencing clomiphene in order to produce a withdrawal bleed. The clinic will advise you on the appropriate monitoring that you will need during the cycle to confirm ovulation. A low dose of clomiphene is used in the first cycle and this is gradually increased each cycle until ovulation is achieved.
Ovulation Induction with FSH Ovulation induction with gonadotrophin therapy is a medical treatment designed to stimulate the ovaries to produce a single mature follicle, to induce ovulation, and to allow fertilisation to occur following intercourse. There are a number of conditions which result in loss of the ability to mature eggs in the ovary and irregular or absent periods. Most of these are treatable with ovulation induction.
1.Hypothalamic Amenorrhoea Some women don’t ovulate because the ovaries are not exposed to enough hormones produced by their own pituitary glands. Deficiencies of these hormones can occur because of pituitary damage but they commonly result because the body is trying to conserve energy or cope with stress. (Women with a tendency to this include those who are underweight, who exercise a lot or who are subject to a lot of stress). Additional hCG injections may be required in this situation and will be advised by the clinic.
2. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Other women fail to ovulate because their ovaries are overstimulated to produce excessive amounts of male hormone which interferes with the egg ripening process.
3. Hyperprolactinaemia Some women lose their ability to ovulate because they make too much milk hormone (Prolactin). This can occur with the use of certain prescribed drugs, because of thyroid or kidney disease or as a result of a small benign growth on the pituitary gland.
4. Failure to ovulate on other fertility drugs eg clomiphene citrate The treatment cycle for ovulation induction with gonadotropins involves:
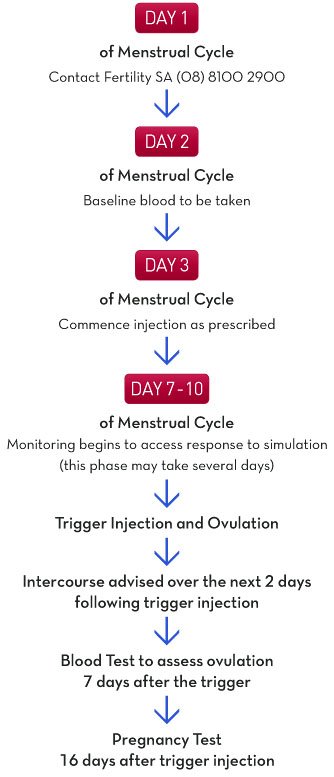
1. Ovarian Stimulation The medication used to stimulate the ovaries is recombinant Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) - Puregon® or Gonal F®. This drug promotes the growth of a follicle within the ovary and is given daily as a subcutaneous injection into either the thigh or the abdomen. These injections commence on day 2 or 3 of your menstrual cycle. The dose prescribed depends on your age, weight and underlying medical condition.
2. Cycle Monitoring As the follicle grows it produces the hormone oestrogen which can be measured in the blood. Therefore blood tests tell us how your ovaries are responding to treatment and allow us to modify treatment where necessary. The number and size of the follicles on the ovaries will be measured by ultrasound. The ultrasound is performed using a probe inserted into the vagina. This procedure requires an empty bladder. You may have several ultrasounds in a treatment cycle. There are no restrictions on having sexual intercourse during the stimulation phase of the cycle.
3. Ovulation Once the follicle has reached the desired size the FSH injections will be ceased and you will be required to have an injection of hCG. hCG acts to complete the maturation (ripening) of the oocyte within the follicle and to initiate changes in the follicle which lead to ovulation. The nursing staff will advise you of the appropriate time to have intercourse.
4. Luteal Phase You will be required to have a blood test to confirm ovulation approximately 10 days after you have had your hCG injection. If your period commences it is important to contact the nursing staff in the clinic. We understand that this is a very emotional time and it may be helpful for you to speak with the counsellor. We can also arrange for you to speak with your clinic doctor or counsellor about your cycle. If you wish, arrangements can be made for further treatment.
If your period has not commenced approximately 16 days after ovulation a pregnancy test will be performed. The progress of the pregnancy may be assessed by weekly hCG measurements until approximately eight weeks of pregnancy (about 3 weeks after the missed period). An ultrasound of the pelvis is then performed, by which time the pregnancy sac and the fetus within should be visible and a fetal heartbeat can be identified.
Introduction
Ovulation Induction with Clomiphene
In situations where the female partner is not ovulating, clomiphene citrate (Clomid® or Serophene®) is often the first line treatment to restore ovulation. Clomiphene causes the pituitary gland in the brain to produce more Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) than happens in the natural cycle; this in turn stimulates the ovaries to produce more eggs.
It is usually administered between day 2 and 6 of the menstrual cycle. In women who have very irregular periods a progesterone medication such as Primolut® or Provera® may be administered for 10 days prior the commencing clomiphene in order to produce a withdrawal bleed. The clinic will advise you on the appropriate monitoring that you will need during the cycle to confirm ovulation. A low dose of clomiphene is used in the first cycle and this is gradually increased each cycle until ovulation is achieved.
Ovulation Induction with FSH
Ovulation induction with gonadotrophin therapy is a medical treatment designed to stimulate the ovaries to produce a single mature follicle, to induce ovulation, and to allow fertilisation to occur following intercourse. There are a number of conditions which result in loss of the ability to mature eggs in the ovary and irregular or absent periods. Most of these are treatable with ovulation induction.
1.Hypothalamic Amenorrhoea
Some women don’t ovulate because the ovaries are not exposed to enough hormones produced by their own pituitary glands. Deficiencies of these hormones can occur because of pituitary damage but they commonly result because the body is trying to conserve energy or cope with stress. (Women with a tendency to this include those who are underweight, who exercise a lot or who are subject to a lot of stress). Additional hCG injections may be required in this situation and will be advised by the clinic.
2. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
Other women fail to ovulate because their ovaries are overstimulated to produce excessive amounts of male hormone which interferes with the egg ripening process.
3. Hyperprolactinaemia
Some women lose their ability to ovulate because they make too much milk hormone (Prolactin). This can occur with the use of certain prescribed drugs, because of thyroid or kidney disease or as a result of a small benign growth on the pituitary gland.
4. Failure to ovulate on other fertility drugs eg clomiphene citrate
The treatment cycle for ovulation induction with gonadotropins involves:
1. Ovarian Stimulation
The medication used to stimulate the ovaries is recombinant Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) - Puregon® or Gonal F®. This drug promotes the growth of a follicle within the ovary and is given daily as a subcutaneous injection into either the thigh or the abdomen. These injections commence on day 2 or 3 of your menstrual cycle. The dose prescribed depends on your age, weight and underlying medical condition.
2. Cycle Monitoring
As the follicle grows it produces the hormone oestrogen which can be measured in the blood. Therefore blood tests tell us how your ovaries are responding to treatment and allow us to modify treatment where necessary. The number and size of the follicles on the ovaries will be measured by ultrasound. The ultrasound is performed using a probe inserted into the vagina. This procedure requires an empty bladder. You may have several ultrasounds in a treatment cycle. There are no restrictions on having sexual intercourse during the stimulation phase of the cycle.
3. Ovulation
Once the follicle has reached the desired size the FSH injections will be ceased and you will be required to have an injection of hCG. hCG acts to complete the maturation (ripening) of the oocyte within the follicle and to initiate changes in the follicle which lead to ovulation. The nursing staff will advise you of the appropriate time to have intercourse.
4. Luteal Phase
You will be required to have a blood test to confirm ovulation approximately 10 days after you have had your hCG injection. If your period commences it is important to contact the nursing staff in the clinic. We understand that this is a very emotional time and it may be helpful for you to speak with the counsellor. We can also arrange for you to speak with your clinic doctor or counsellor about your cycle. If you wish, arrangements can be made for further treatment.
If your period has not commenced approximately 16 days after ovulation a pregnancy test will be performed. The progress of the pregnancy may be assessed by weekly hCG measurements until approximately eight weeks of pregnancy (about 3 weeks after the missed period). An ultrasound of the pelvis is then performed, by which time the pregnancy sac and the fetus within should be visible and a fetal heartbeat can be identified.